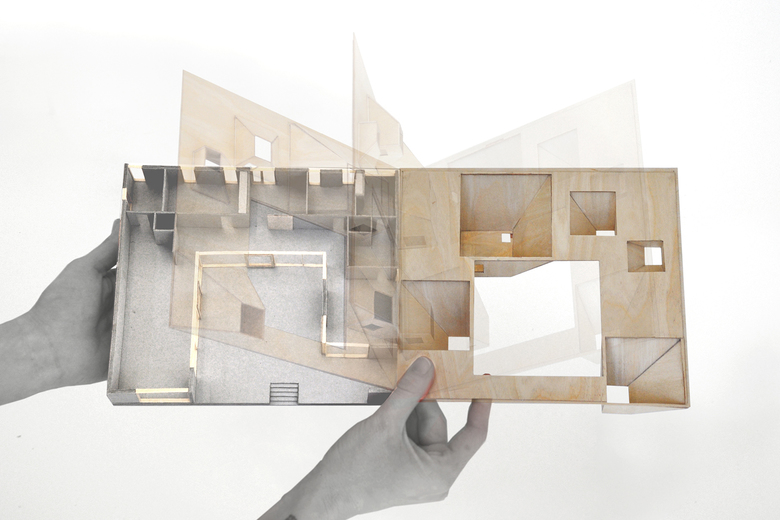
Laser Cutting for Accurate Architectural Model Making
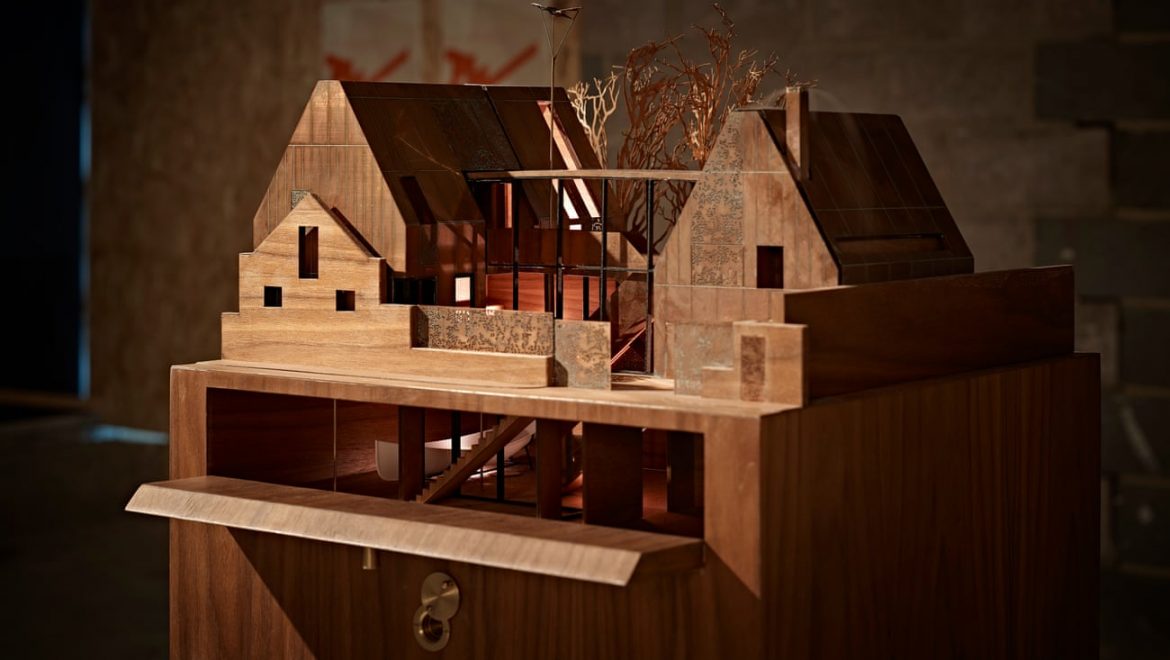
Laser cutting is a precise and efficient technique used in architectural model making to create accurate and detailed models. Laser cutting involves the use of a high-powered laser to cut through materials such as wood, acrylic, and cardboard with great precision, creating clean and accurate cuts.
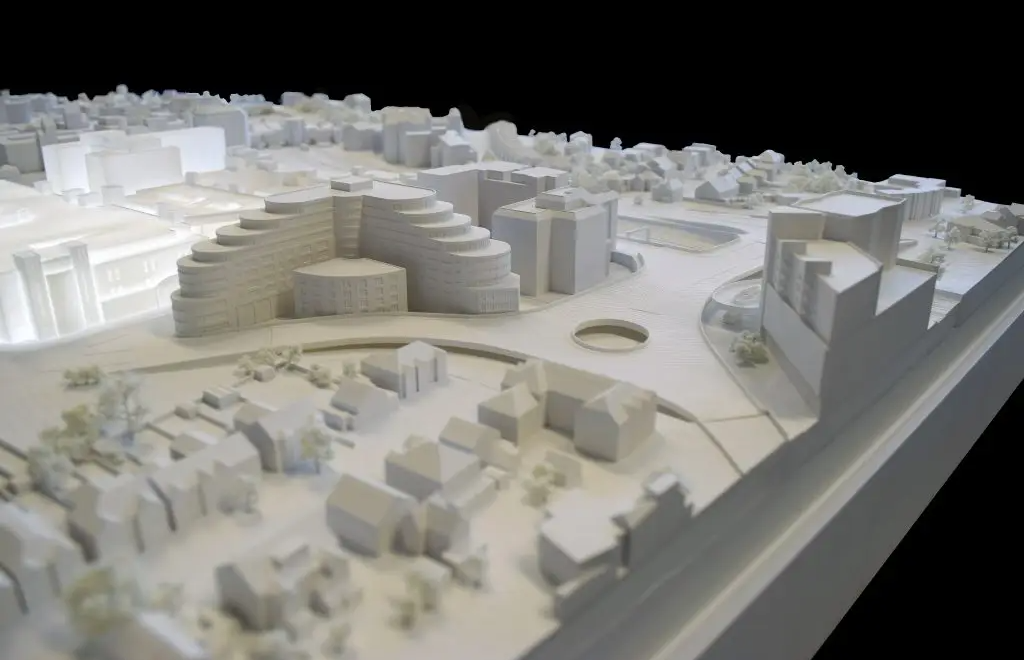
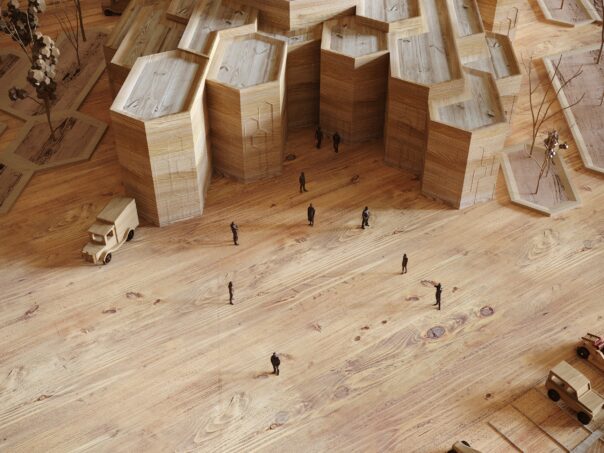
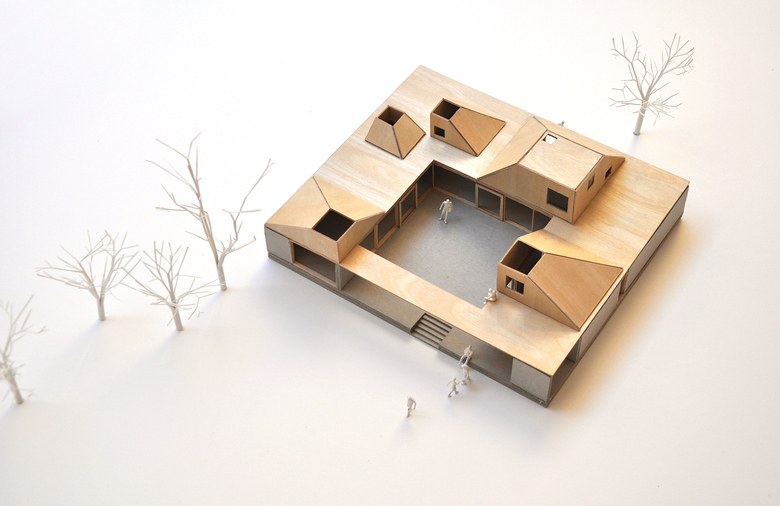
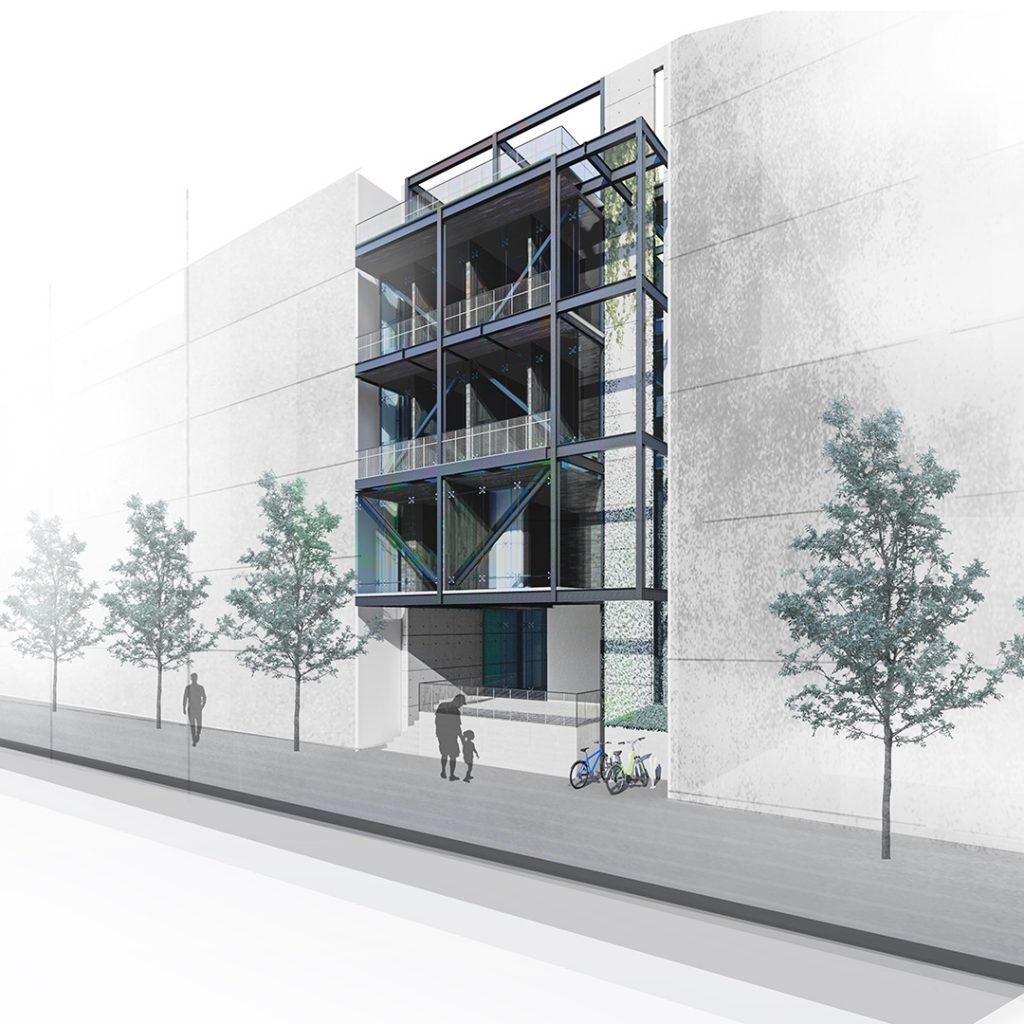
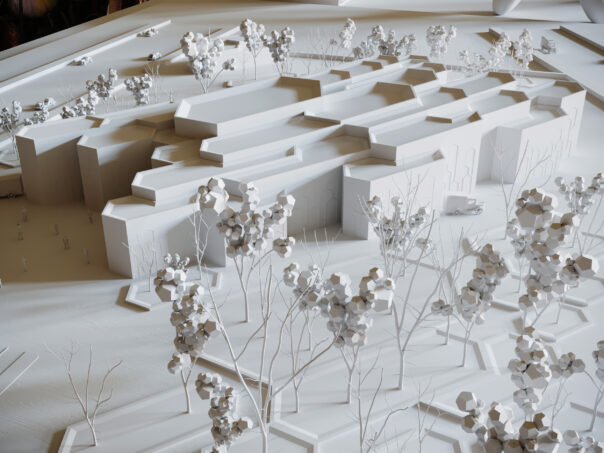
In architectural model making, laser cutting is commonly used to create components such as walls, roofs, and floors, as well as intricate details such as windows and doors. The laser cutter can also be used to etch or engrave details onto the surface of the model, creating texture and depth.
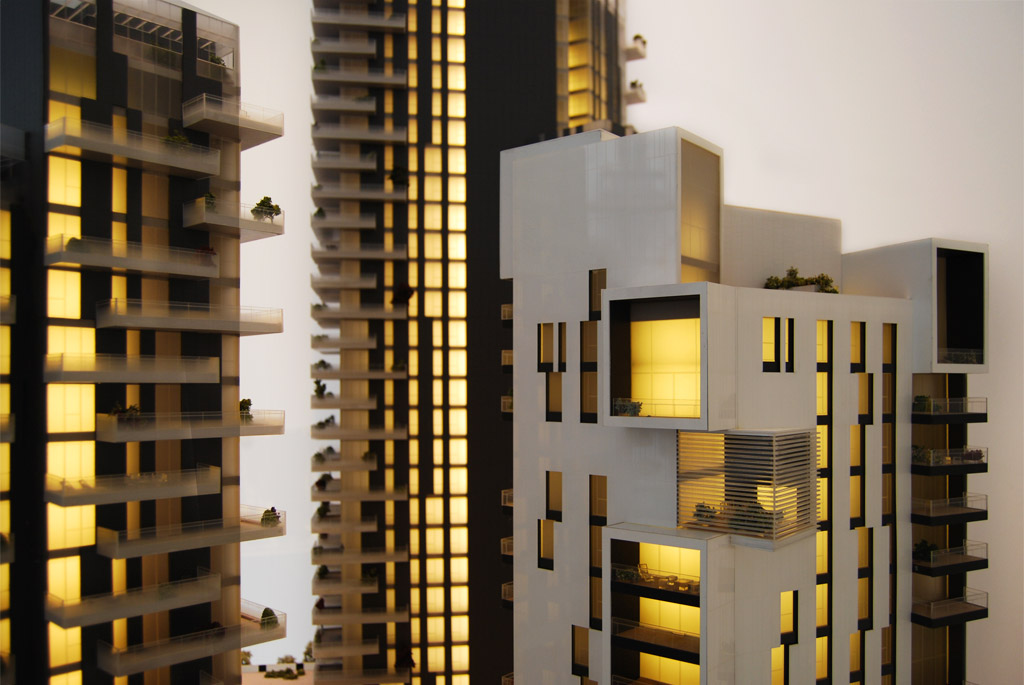
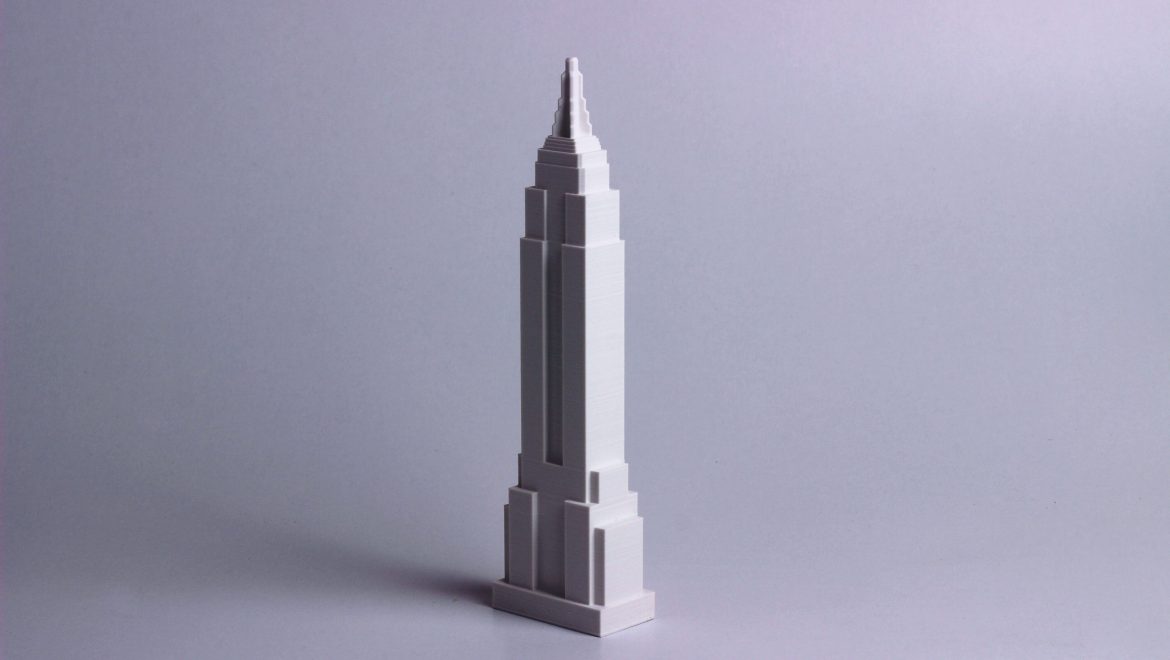
One of the main advantages of laser cutting in architectural model making is the level of precision that can be achieved. Laser cutting machines can cut materials with great accuracy, making it possible to create complex and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional model making techniques.
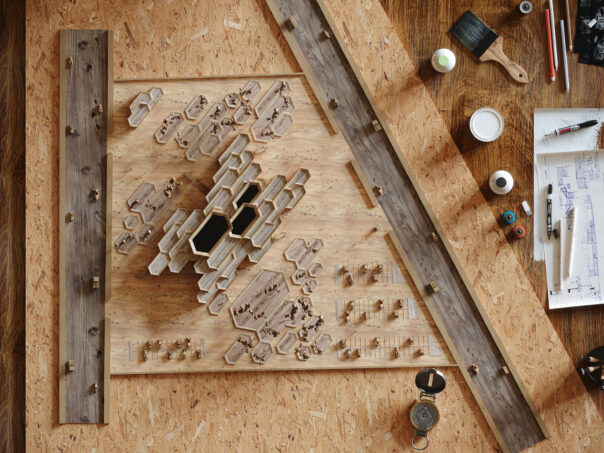
Laser cutting also offers a high degree of efficiency in architectural model making. The machines are capable of cutting multiple components simultaneously, allowing for the rapid production of components and reducing the amount of time needed to create a model.
Another advantage of laser cutting is the ability to work with a wide range of materials. Laser cutters can cut through a variety of materials, including wood, acrylic, cardboard, and even metal, allowing for flexibility in the design and construction of the model.
Overall, laser cutting is an effective and efficient technique in architectural model making, providing precision, speed, and versatility in the creation of accurate and detailed models.